Laboratory plastic consumables are indispensable tools in modern scientific research. These disposable items, such as Pipette Tips and Deep Well Plates, streamline laboratory workflows by ensuring sterility and precision. Made from durable polymers like polypropylene and polystyrene, they support diverse applications, including sample storage, chemical reactions, and diagnostics. Their design minimizes contamination risks and enhances compatibility with laboratory instruments, improving safety and efficiency. High-quality consumables meet strict manufacturing standards, delivering consistent results. Whether you’re conducting microbiological testing or chemical analysis, these tools are essential for maintaining accuracy and reliability in your experiments.
For more information or assistance, Contact Us today.
Key Takeaways
- Lab plastic tools, like pipette tips and petri dishes, are important for accurate and reliable experiments.
- Pick the right tools by knowing your task and using materials that prevent contamination or mistakes.
- Use high-quality, certified products to make your lab work safer and more precise.
- Help the environment by choosing reusable or biodegradable tools to cut down on plastic waste.
- Learn about new lab tools to work faster and meet new research needs.
Types of Laboratory Plastic Consumables
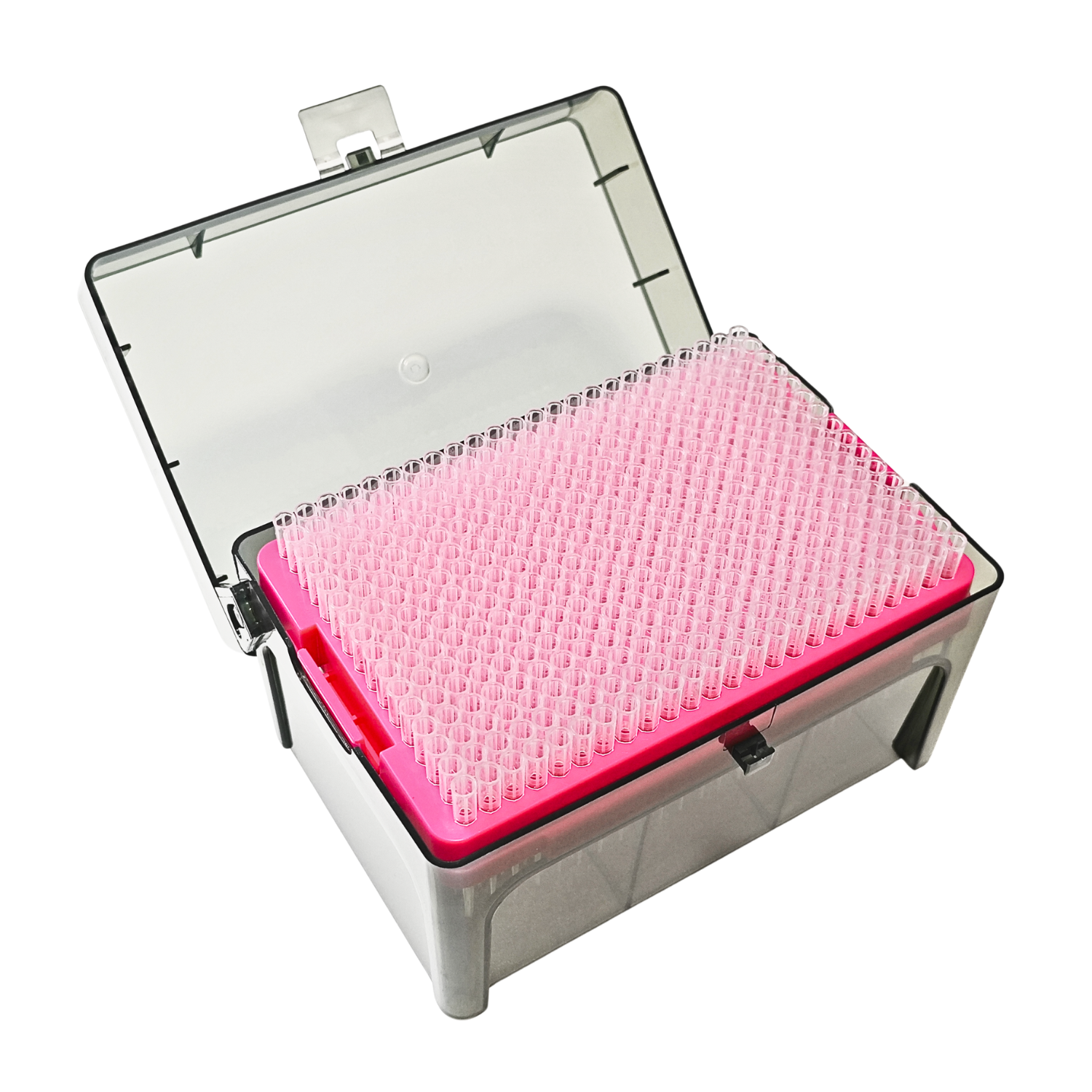


Laboratory plastic consumables play a vital role in modern scientific research. These items are classified into several categories based on their applications, including reagent consumables, cell culture consumables, and molecular biology experimental consumables. Below, you will find an overview of three essential types of consumables and their specific uses.
Pipettes and Pipette Tips
Pipettes and pipette tips are indispensable tools for transferring liquids in laboratories. They ensure precision and reproducibility, which are critical for experiments requiring accurate liquid handling. You can use pipette tips to prevent contamination, as they act as a barrier between the sample and the pipette. This feature is especially important for techniques like PCR, where cross-contamination can compromise results. Disposable pipette tips save time by eliminating the need for washing and sterilization. Their availability in various sizes and formats makes them convenient for diverse applications, from molecular biology to chemical analysis.
Petri Dishes
Petri dishes are essential for microbiology and cell culture experiments. These shallow, cylindrical containers provide an ideal environment for growing microorganisms or cells. You can use them to observe bacterial colonies, test antibiotic effectiveness, or study cell behavior. Sterile plastic petri dishes are preferred over glass alternatives due to their disposable nature, which reduces contamination risks. Their lightweight design also makes them easier to handle during experiments. Whether you are conducting research in microbiology or teaching students about microbial growth, petri dishes are a fundamental tool.
Centrifuge Tubes
Centrifuge tubes are designed for separating components in a sample through centrifugation. Plastic centrifuge tubes offer several advantages over glass ones. They are lightweight, shatterproof, and chemically resistant, making them safer and more versatile. You can use them for various applications, such as isolating DNA, proteins, or other biomolecules. Disposable options eliminate the need for cleaning, saving time and reducing contamination risks. Their transparent design allows you to monitor the contents easily, ensuring accurate results. These features make plastic centrifuge tubes a cost-effective and reliable choice for laboratories.
Microplates
Microplates are indispensable in laboratories, especially for high-throughput screening (HTS) and diagnostic assays. These versatile tools allow you to conduct multiple biological or chemical reactions simultaneously, saving time and resources. Microplates come in various formats, such as 96-well and 384-well plates, each designed to meet specific experimental needs. For instance, the 384-well Small Volume microplate enhances reagent efficiency by accommodating more wells within the same footprint. This feature makes it ideal for fluorescence and luminescence assays.
When selecting a microplate, you should consider factors like well number, volume, and surface treatments. These attributes directly impact assay performance. For high-content screening and microscopy, microtiter plates with cycloolefin film bottoms ensure maximum resolution and consistent cell attachment. Proper handling, including mixing and incubation, is also crucial for reliable results. By choosing the right microplate, you can optimize your experiments and achieve consistent outcomes.
Beakers and Cuvettes
Beakers and cuvettes are fundamental laboratory plastic consumables used for handling liquids. Beakers, with their wide mouths and flat bottoms, are perfect for mixing, heating, or transferring solutions. Their graduated markings help you measure volumes with ease. Plastic beakers, often made from polypropylene, are lightweight, durable, and resistant to chemicals, making them suitable for various laboratory tasks.
Cuvettes, on the other hand, are essential for spectrophotometry. These small, transparent containers hold liquid samples for optical analysis. Plastic cuvettes, typically made from polystyrene or polymethyl methacrylate, are cost-effective and disposable, reducing the risk of contamination. Whether you are measuring absorbance or fluorescence, cuvettes ensure accurate and reproducible results.
Other Consumables (e.g., cryovials, test tubes, filter tips)
Laboratories rely on a wide range of other consumables to support diverse applications. Here are some examples:
| Consumable Type | Function | Materials | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cryovials and Cryogenic Tubes | Store biological samples at low temperatures. | Polypropylene (PP) | Long-term storage of biological samples. |
| Test Tubes | Hold, mix, or heat chemicals and biological samples. | Polypropylene (PP), polystyrene (PS), polyethylene terephthalate (PET) | Chemical reactions, microbiology, and sample analysis. |
| Filter Tips | Prevent contamination during liquid handling. | Polypropylene (PP) | PCR, molecular biology, and diagnostics. |
These consumables enhance laboratory efficiency by offering specialized solutions for storage, analysis, and liquid handling. For instance, cryovials ensure the safe preservation of biological samples, while filter tips minimize contamination risks during sensitive procedures. By incorporating these tools into your workflow, you can maintain precision and reliability in your experiments.
Types of Laboratory Plastic Consumables
Precision and Accuracy
You rely on laboratory plastic consumables to achieve precise and accurate results in your experiments. Their design and manufacturing processes ensure tight tolerances and controlled purity, which are critical for reproducibility. These consumables withstand mechanical and thermal loads, making them suitable for demanding applications. Their high chemical resistance prevents reactions with samples, preserving the integrity of your results. Additionally, their precision in shape and tightness ensures compatibility with laboratory instruments, reducing errors. By using consumables designed to prevent leaching of harmful substances, you can maintain the reliability of your experiments.
Safety and Contamination Prevention
Safety and contamination prevention are essential in any laboratory setting. Laboratory plastic consumables, such as pipette tips and centrifuge tubes, are typically sterile before use. This sterility ensures that your samples remain uncontaminated, preserving the integrity of your results. Their single-use nature eliminates the risk of cross-contamination between experiments. For instance, disposable consumables prevent residues or microorganisms from previous trials from affecting new experiments. You can confidently use these tools for sample collection, preparation, and storage, knowing they maintain a safe and controlled environment.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
The environmental impact of laboratory plastic consumables is a growing concern. Laboratories generate over 12 billion pounds of plastic waste annually, contributing significantly to global pollution. For example, producing a single 96-rack of polypropylene pipette tips releases approximately 0.304 kg of CO2 equivalent and consumes about 6.6 liters of water. However, sustainable practices are emerging to address these challenges. Bioplastics, expected to occupy 40% of the plastic industry by 2030, offer a promising alternative. Biomass-derived polymers are also being developed to replace non-biodegradable plastics. Adopting a circular economy framework, as seen in the Genever Lab at the University of York, can significantly reduce waste. By streamlining recycling processes and switching to smaller multiwell plates, they reduced plastic waste by up to 1,000 kilograms annually. You can contribute to sustainability by choosing eco-friendly consumables and implementing waste reduction strategies in your laboratory.
Materials Used in Laboratory Plastic Consumables
Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene (PP) is one of the most commonly used materials in laboratory plastic consumables due to its exceptional properties. You will find it lightweight and easy to handle, which reduces strain during repetitive tasks. Its high chemical resistance makes it suitable for handling acids, bases, and solvents, though it is not ideal for strong oxidizers. PP is also autoclavable, allowing you to sterilize it at 121°C without compromising its integrity. This feature ensures safe and reusable options for applications requiring sterility.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| High Chemical Resistance | Resistant to most acids, bases, and solvents; not suitable for strong oxidizers. |
| Autoclavable | Can be sterilized at 121°C and 15 psi for 15 minutes. |
| Lightweight | Easy to handle and reduces overall weight in lab settings. |
PP’s durability and cost-effectiveness make it a preferred choice for items like centrifuge tubes, pipette tips, and cryovials. Its FDA approval for food contact further highlights its safety and versatility.
Polystyrene (PS)
Polystyrene (PS) is another material widely used in laboratory plastic consumables. Its transparency allows you to easily observe samples, making it ideal for applications like petri dishes and culture tubes. PS is colorless and hard, but it lacks flexibility and is prone to brittleness. While it offers moderate chemical resistance, it is unsuitable for strong acids, bases, or organic solvents.
| Property | Polystyrene (PS) |
|---|---|
| Durability | Brittle, lacks chemical resistance, not heat-resistant. |
| Transparency | Transparent, ideal for visual sample observation. |
| Applications | Petri dishes, culture tubes, disposable pipettes. |
You should consider PS for tasks where visibility and disposability are priorities, but avoid using it in high-temperature or chemically aggressive environments.
Polyethylene (PE) and Other Materials
Polyethylene (PE) stands out for its versatility and durability. It resists stress cracking and retains flexibility, even under challenging conditions. PE’s excellent chemical resistance makes it suitable for handling organic solvents and electrolytic substances. Additionally, its recyclability aligns with sustainable laboratory practices.
Polyethylene is the most widely used plastic globally due to its impact strength and ability to stretch without breaking. It resists most alkalis and acids, making it a reliable choice for laboratory applications.
Other materials like high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and low-density polyethylene (LDPE) also contribute to laboratory plastic consumables. These materials, along with PP and PS, provide a range of options tailored to specific experimental needs.
How to Choose the Right Laboratory Plastic Consumables
Consider the Application
Selecting the right laboratory plastic consumables begins with understanding your specific application. Each experiment or procedure has unique requirements, and the consumables you choose must align with these needs. For instance, if you work with high-speed centrifugation, opt for centrifuge tubes that can withstand strong centrifugal forces. Similarly, applications involving optical analysis demand consumables with high transparency, such as polystyrene cuvettes.
You should also evaluate the functional properties of the consumables. Look for features like tightness, precision, and durability. These attributes ensure reliable performance and reduce the risk of errors during experiments. While cost is a factor, prioritize efficiency and longevity over initial purchase price. Balancing upfront costs with long-term operational benefits will help you make a more informed decision.
Evaluate Material Compatibility
Material compatibility plays a crucial role in ensuring the success of your experiments. Different materials offer varying levels of chemical, thermal, and mechanical resistance. For example, polypropylene is ideal for handling acids and bases due to its high chemical resistance, while polyethylene excels in flexibility and durability. If your work involves sterilization, choose consumables made from autoclavable materials like polypropylene.
To avoid complications, match the material properties to your experimental conditions. Consider factors such as chemical compatibility, transparency, and flexibility. Using incompatible materials can lead to sample degradation or compromised results. By carefully evaluating these aspects, you can select consumables that meet the demands of your laboratory environment.
Assess Quality and Certification
Quality and certification are non-negotiable when choosing laboratory plastic consumables. Products certified by regulatory bodies like the FDA, ISO, or CE meet stringent quality standards, ensuring reliability and safety. Always verify that the supplier adheres to relevant ISO quality standards.
Additionally, inspect the consumables for signs of aging or defects. High-quality products should maintain their structural integrity over time. Ensure that the raw materials, such as polypropylene or polyethylene, comply with modern laboratory requirements. By prioritizing certified and high-quality consumables, you can enhance the accuracy and safety of your experiments.
Factor in Sustainability
Sustainability plays a critical role in the selection of laboratory plastic consumables. As laboratories generate significant amounts of plastic waste, you must consider the environmental impact of your choices. Researchers estimate that biomedical and agricultural laboratories alone produce approximately 5.5 metric tonnes of plastic waste annually. This highlights the urgent need for adopting sustainable practices in laboratory operations.
One effective approach involves transitioning to a closed-loop system. By washing and reusing consumables like pipette tips and plates, you can significantly reduce waste without compromising quality. Studies from the NIH and CDC confirm that reused tips maintain the same performance standards as new ones. This method not only minimizes environmental impact but also reduces costs over time.
Manufacturers are also addressing sustainability concerns by developing innovative materials. Bioplastics and biodegradable options are becoming increasingly available, offering you eco-friendly alternatives to traditional plastics. These materials are projected to make up 40% of the plastic industry by 2030, signaling a major shift toward greener laboratory practices. Choosing such options allows you to align your laboratory operations with global sustainability goals.
In addition to material choices, you can adopt waste reduction strategies to further enhance sustainability. For instance, switching to smaller multiwell plates or optimizing experimental designs can decrease the volume of consumables used. Recycling programs tailored for laboratory plastics also provide an effective way to manage waste responsibly.
By factoring sustainability into your decision-making process, you contribute to reducing the environmental footprint of your laboratory. Opting for reusable consumables, biodegradable materials, and efficient waste management practices ensures that your work supports both scientific progress and environmental stewardship.
Laboratory plastic consumables play a pivotal role in enhancing efficiency, precision, and safety in scientific research. These tools ensure accuracy and reliability in experiments, as seen during the COVID-19 pandemic when shortages of pipette tips and gloves disrupted critical projects. Their availability supports seamless workflows and minimizes contamination risks, making them indispensable in laboratories.
You can choose from a wide range of consumables, including pipette tips, centrifuge tubes, and microplates, each tailored for specific applications. Selecting the right consumables requires careful consideration of factors like chemical resistance, transparency, and durability. Prioritizing quality and sustainability ensures long-term efficiency while reducing environmental impact. By making informed choices, you can optimize laboratory operations and support sustainable practices.
Post time: Feb-15-2025